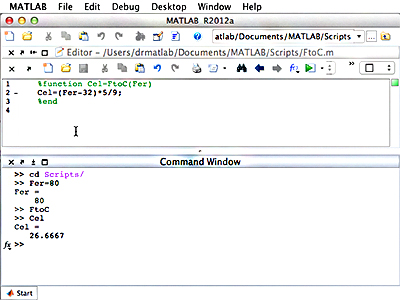
Screenshot of a function definition to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius and the respective function call.
Another convenience of MATLAB® is its ability to manipulate complex numbers, such that you can take powers and roots of any number. For practice, you will be asked to calculate and plot the basins of attraction for a polynomial in the complex plane.
Also in this unit, you will learn how to create a user-defined function in MATLAB. It is important to understand the difference between a script and a function. While a script is a separate piece of code that performs a certain task, it deals with the variables from the caller, and cannot accept input values or provide return values. Functions, on the other hand, can receive an input and deliver an output, and the variables contained therein are isolated from those of the caller. In determining whether a script or function should be used, you will need to consider the scope of the variable. Within a function, variables exist within that small space of code, and values changed within the lines of code in the function will not affect those outside in the calling workspace.
With this knowledge, your first task will be to write a function that calculates the Fibonacci numbers. This function will be recursive, meaning that it calls itself, because each Fibonacci number is calculated by taking the sum of the previous two Fibonacci numbers in the sequence.
As an exercise, you will be given a piece of code that calculates and plots the solution to the Van-der-Pol oscillator. You will also be given a series of tasks by which to edit the code and resulting plot, and later, to debug the code.
Related Videos
The videos below demonstrate, step-by-step, how to work with MATLAB in relevance to the topics covered in this unit.
-
Lecture 5: Scripts and Functions
This video includes material supplementary to Scope. -
Lecture 6: Debugging
This video includes material supplementary to Scope, Homework 3.
